Diamond professionals use a special set of four value factors to describe and classify diamonds: Carat Weight、Color、Clarity、Cut. These are knows as the Four Cs. WHen used together, They describe the quality of a finished diamonds, which is directly related to its value.
Diamond weights are stated in metric carats, abbreviated "cts." One metric carat is one-fifth(0.200) of a gram.

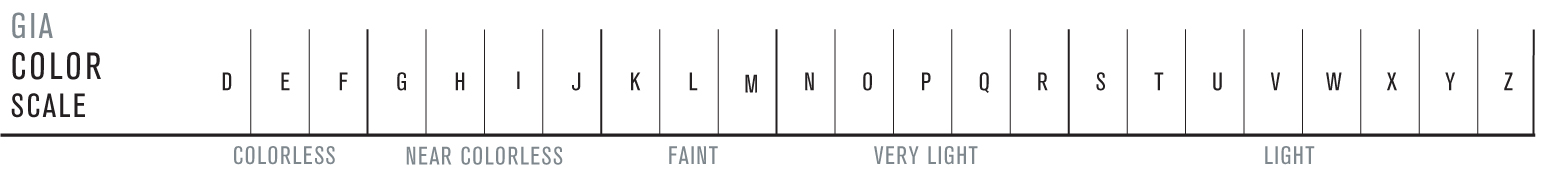
The Color scale begins with D(colorless) and continues through the alphabet to Z(light yellow). Within the D-to-Z range, when all other value factors are equal, colorless diamonds are the most valuable.
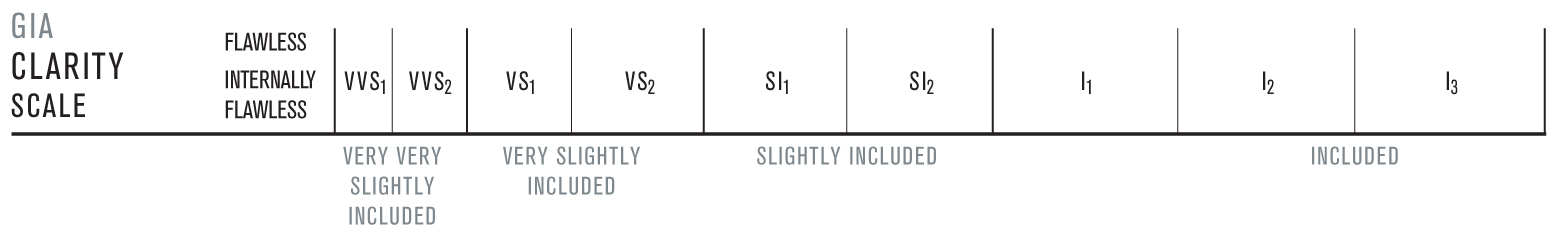
Clarity is a gemstone's relative freedom from clarity characteristics, which are classified as inclusions and blemishes.
Clarity charateristics make every diamond unique. It's extremely unlikely that two diamonds would have exactly the same clarity characteristics in identical locations. This helps you to identify individual diamonds and tell one diamond from another.
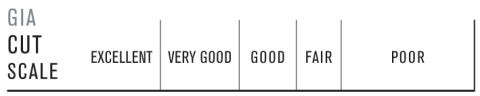
The way a diamond is cut can affect its clarity, and even its color. Cut governs the interaction between a diamond and the light around it, and that intereaction determines the diamond's overall appearance.
The round brilliant offers an excellent display of light performance. It's a classic that's always in fashion. It's the shape everyone thinks of when they picture a diamond. The facet arrangement hides inclusions. And there are generally more sizes to choose from than there are for any other shpe.